Databricks, a data science and AI company, has recently released DBRX, the most potent open-source large language model. This achievement marks a significant step forward in the field of open-source AI, potentially accelerating innovation and scientific understanding.
DBRX Development Process
The creation of DBRX involved months of work and a significant investment of around $10 million. The core team, led by chief neural network architect Jonathan Frankle, designed DBRX based on the transformer architecture, a robust neural network framework for language processing.
Training a model like DBRX requires massive amounts of data and computational power. Databricks leveraged 3,072 powerful Nvidia H100s GPUs to train DBRX on a vast dataset of text and code. The team meticulously monitored the training process, making critical decisions about utilizing the remaining compute time towards the end. Ultimately, they opted for a “curriculum learning” approach, fine-tuning the model on curated data to enhance specific capabilities.
Opensource vs. Closed Source
Traditionally, leading AI companies like OpenAI and Google have kept their large language models, such as GPT-4 and Gemini, under close wraps. However, Databricks is committed to open-source development, believing it fosters innovation by allowing researchers, startups, and established businesses more comprehensive access to this technology. Additionally, Databricks plans to share details about the development process, promoting greater transparency in the field.
This commitment to openness aligns with the views of organizations like EleutherAI, a collaborative open-source AI research project. They argue that open models can accelerate scientific progress and economic growth, while concerns about potential misuse have yet to be substantiated.
DBRX
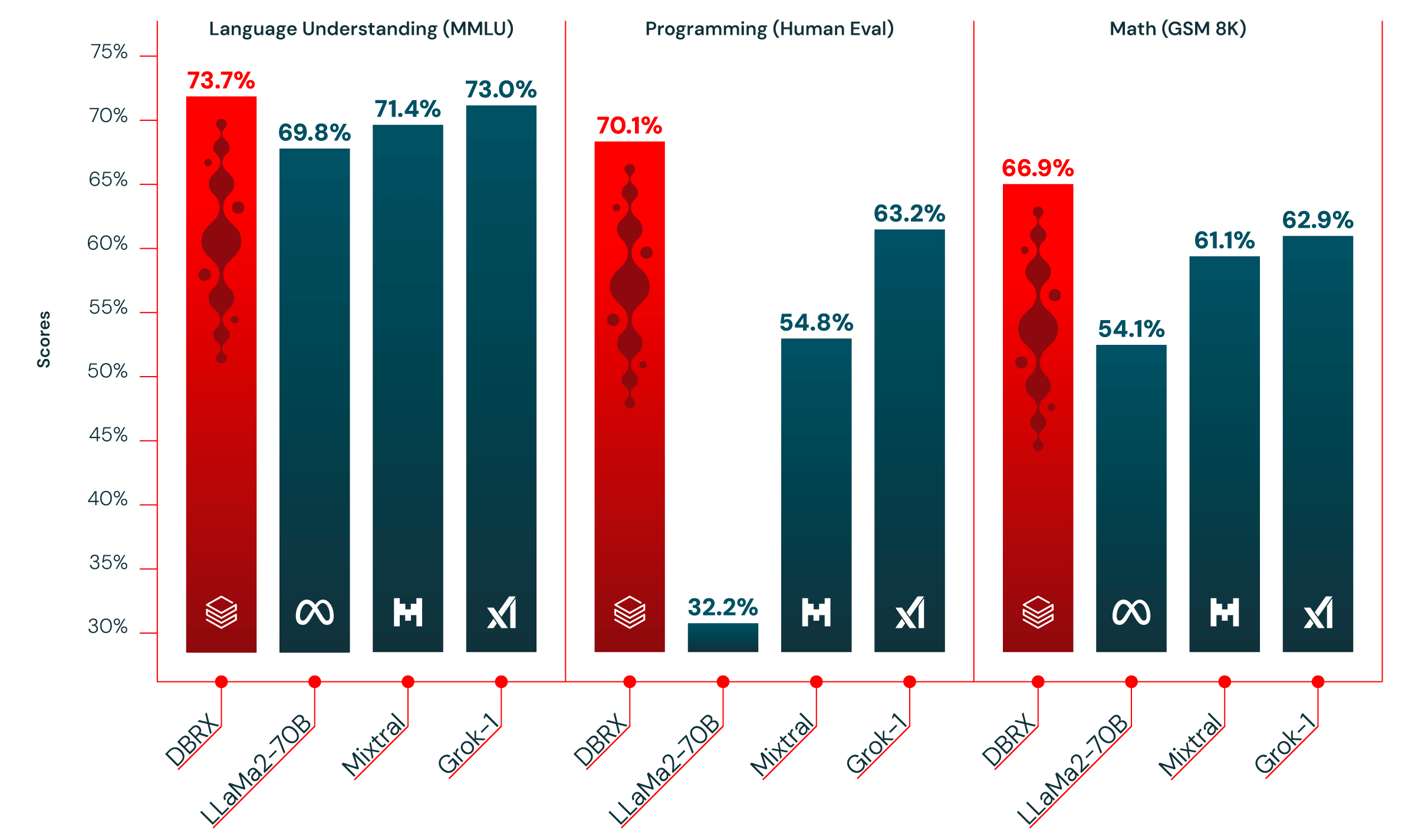
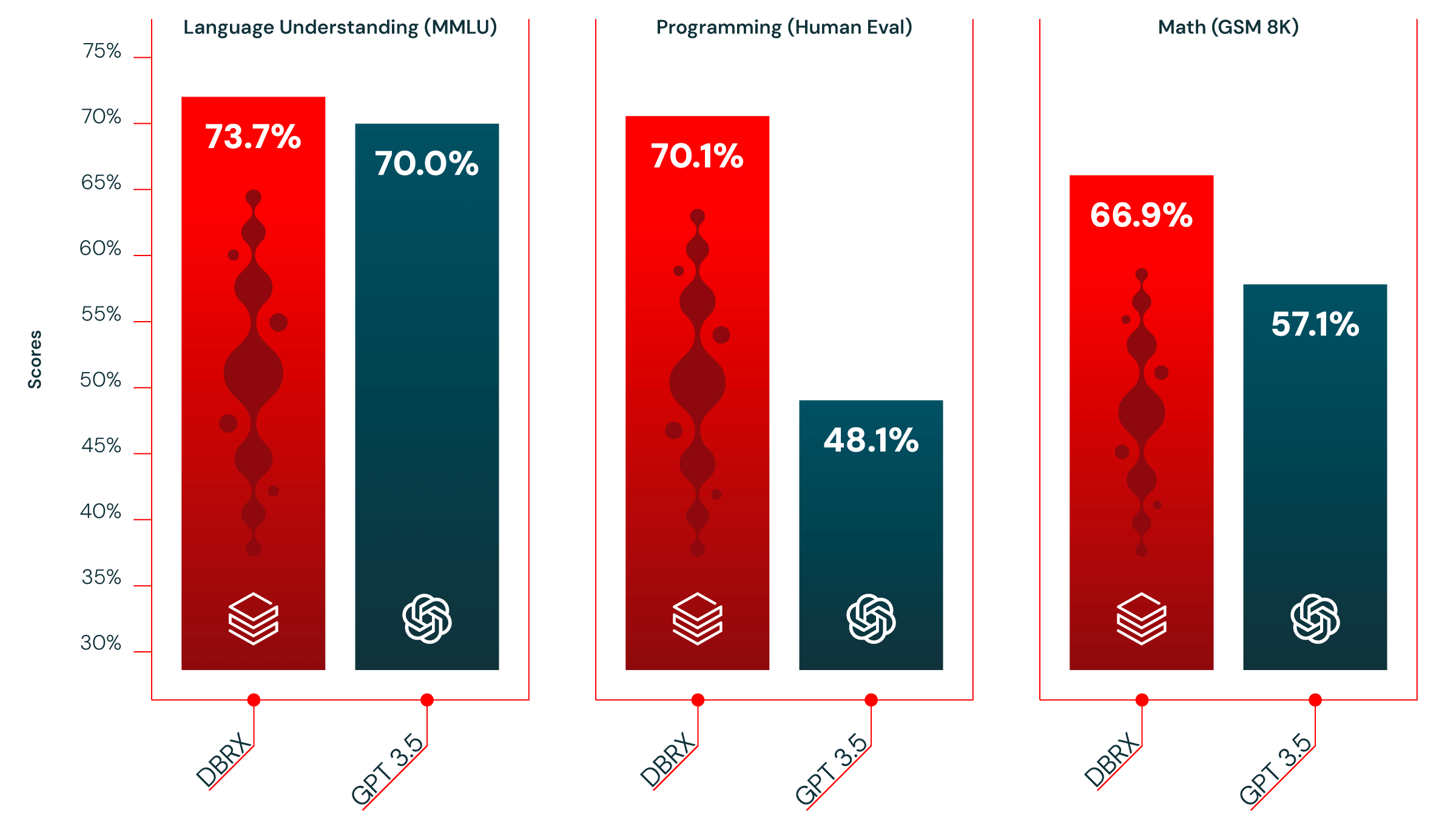
DBRX surpassed expectations, outperforming open-source models like Meta’s Llama 2 and Mistral’s Mixtral on various benchmarks. Notably, it even rivaled OpenAI’s closed-source GPT-4 in some areas. This achievement positions DBRX as a valuable tool for researchers and businesses.
Databricks envisions DBRX applications in various sectors, particularly finance and medicine. They offer customization options, allowing companies to tailor DBRX to their needs while addressing concerns about sending sensitive data to the cloud.
The impressive performance of DBRX, achieved through efficient model architecture and training techniques, demonstrates the potential for cost reductions in AI development. This, coupled with the availability of open-source models like DBRX, suggests a future of rapid advancement in AI.
The Inner Workings of an LLM
At its core, DBRX is a giant artificial neural network loosely mimicking the structure and function of the human brain. This network is trained on massive amounts of text data, allowing it to process information and generate human-quality text in response to various prompts and questions.
The transformer architecture plays a crucial role in DBRX’s capabilities. Invented by Google researchers in 2017, this architecture revolutionized machine learning for language tasks.
Beyond architecture, the data used to train a model significantly impacts its performance. While Databricks remains tight-lipped about the specifics of their dataset, they acknowledge the importance of data quality and careful preparation.
Recent advancements in AI research have introduced the concept of a “mixture of experts.” This approach involves activating only specific parts of the model depending on the query, leading to a more efficient and performant system. DBRX utilizes this technique to achieve significant efficiency gains.
Human Involvement in DBRX
Technical considerations only partially drove the development of DBRX. The team faced crucial decisions that required a blend of technical expertise and intuition. A pivotal example involved the final week of training, which had significant computing resources remaining. The team debated between various approaches, including code generation model specialization, curriculum learning, and scaling up the model further. Ultimately, Frankle steered the team towards the data-centric approach of curriculum learning, a decision that proved highly successful.
Another instance involved Frankle’s skepticism about DBRX’s code-generation capabilities. He even bet on his hair color, vowing to dye it blue if the model performed well in this area. As it turned out, DBRX excelled in code generation tasks, leaving Frankle with a scheduled hair-dyeing appointment.
Future Considerations
The release of DBRX raises questions about the potential risks associated with open-source AI models. Some experts worry that such models could be misused for malicious purposes. However, advocates like Stella Biderman of EleutherAI argue that open models sometimes pose a more significant threat than closed ones. They believe that transparency can aid in understanding and mitigating potential risks.
Databricks’ achievement with DBRX signifies a significant milestone in open-source AI development. Here’s a look at the broader implications and what the future might hold:
One of the most exciting aspects of DBRX lies in its potential to contribute to a more profound understanding of how AI models learn and evolve. By analyzing the model’s changes during the final training week, researchers can gain insights into how these robust systems acquire new capabilities. This knowledge can pave the way for developing even more sophisticated and versatile AI models.
Democratization of AI
Open-source models like DBRX make AI technology more accessible to a broader range of players. This empowers startups, small businesses, and even individual researchers to leverage the power of AI without the massive financial resources typically required. This broader accessibility can foster innovation and accelerate progress in various fields.
The open-source nature of DBRX fosters collaboration within the AI research community. Researchers can build upon the foundation of DBRX by experimenting with different training methods and data sets. This collaborative approach can lead to faster advancements and a more comprehensive understanding of AI capabilities.
The Need for Responsible Development
While open-source AI offers numerous benefits, addressing potential risks and ensuring responsible development is crucial. Here are some key considerations:
- Bias Mitigation: AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate those biases in their outputs. Developers and users of DBRX need to be aware of potential biases and take steps to mitigate them.
- Security Concerns: Malicious actors could potentially exploit open-source models for harmful purposes. Robust security measures and best practices are essential to minimize these risks.
- Regulation and Governance: As AI evolves, clear guidelines and regulations might be necessary to ensure responsible development and deployment. Open dialogue and collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and the public will be crucial in shaping a future where AI benefits all of humanity.
The release of DBRX marks a turning point in open-source AI. As researchers continue to explore the potential of this powerful model and its underlying technologies, we can expect to see significant advancements in the field. The key lies in harnessing the power of AI for good, fostering responsible development practices, and ensuring equitable access to this transformative technology.



























